Healthy sperm appear whitish-gray with a mild bleach-like odor. Unhealthy sperm displays yellow, green, red, or brown discoloration, watery or excessively thick consistency, foul odor, or abnormal semen analysis results showing low count or poor motility.
Are you wondering whether your sperm is healthy enough to start a family? You’re not alone. If you’ve been trying for several months without success, you might be questioning whether male fertility could be playing a role—and that’s a smart question to ask. Up to 50 percent of couples struggling to conceive have male factor issues.
Here’s something important to understand: it takes over two months (about 64 days) to produce just one sperm , which means the lifestyle choices you make today directly impact your fertility weeks from now. The good news? Many sperm health issues are fixable when you know what to look for. We’ll walk through what doctors want you to know about identifying potential issues and the steps you can take to help support your sperm quality naturally.
Healthy vs Unhealthy Sperm: Key Takeaways
Understanding sperm health is crucial for fertility success and reveals important insights about your overall wellbeing and future child’s health.
- Sperm quality reflects overall health – Men with higher sperm counts tend to live longer and have lower risks of cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
- Healthy sperm has specific characteristics – Normal semen appears whitish-gray, has no odor, and contains 15+ million sperm per milliliter with 40%+ motility.
- Lifestyle factors significantly impact sperm health – Smoking, excessive alcohol, heat exposure, and poor diet can dramatically reduce sperm count and motility.
- Natural improvements take time but work – Since sperm production takes more than 2 months consistent healthy choices like proper nutrition, exercise, and supplements tend to show best results within 2-3 months.
- Professional testing is recommended after 12 months – If conception hasn’t occurred after a year of trying (6 months if partner is 35+), seek fertility specialist evaluation.
Why sperm health matters beyond fertility
Your sperm tells a bigger story than just your ability to conceive. What fertility specialists have discovered is that sperm quality acts like a health report card—one that can predict everything from your lifespan to your future child’s wellbeing. Understanding your sperm health isn’t just about getting pregnant—it’s about understanding your overall wellness.
Sperm as a marker of overall health
Here’s something most men don’t realize: sperm count directly correlates with how long you’ll live. Research shows that men with higher sperm counts tend to live longer, with mortality rates dropping steadily as sperm concentration increases up to 40 million per milliliter
This connection makes sense when you consider that the same lifestyle factors that harm sperm health often signal or contribute to other chronic conditions. Your reproductive health and overall health are deeply connected.
Links to chronic diseases like diabetes and heart issues
Poor sperm health often acts as an early warning system for chronic conditions. Men with fertility problems have significantly higher risks of developing cardiovascular diseases.
The diabetes connection is particularly concerning. Infertile men show increased risk of developing diabetes, while diabetic men experience higher rates of infertility—creating a cycle that affects both current and future health. Men with low sperm counts typically carry extra weight around their midsection and have higher blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
How sperm quality affects long-term child health
Your sperm doesn’t just carry DNA—it carries the effects of your lifestyle choices. Paternal lifestyle creates epigenetic modifications in sperm that can program your child’s development . DNA damage in sperm has been linked to lower pregnancy rates and potentially affects how embryos develop.
Ready to improve your sperm health? Track your fertility journey together with Premom’s PreDad feature. Our tools help you monitor progress while making positive lifestyle changes.
How can you tell if your sperm is healthy?
Determining whether your sperm is healthy starts with understanding what normal looks like. While some signs are visible at home, getting the complete picture requires professional testing. Let’s break down what healthy sperm should look like and when you need expert analysis.
Visual signs of healthy sperm
Healthy semen typically appears whitish or slightly cloudy with a jelly-like texture. This consistency naturally becomes more liquid within 15-30 minutes after ejaculation.
Watch for concerning colors that could signal problems. Yellow, green, red, or brown semen might indicate infection or bleeding. Consistently thick semen could mean severe dehydration or hormonal imbalance, while excessively watery semen might point to vitamin deficiencies.
What does healthy sperm smell like?
Normal semen may be odorless or have a mild, slightly alkaline odor often compared to, bleach. Some men notice a stronger bleach-like or slightly sweet smell due to fructose content—both are typically normal .
A fishy or foul odor isn’t normal and might indicate an infection. Similarly, an unusually sweet smell could potentially signal diabetes.
When to get a semen analysis
Consider professional testing if you’ve been trying to conceive for 12+ months without success (6+ months if your partner is 35 or older). Other reasons include recurrent pregnancy loss, history of testicular trauma, chemotherapy exposure, or concerning lifestyle factors like chronic alcohol intake, varicoceles, THC use, or steroid use.
Take Premom’s Male Fertility Self-assessment to determine if professional testing might be beneficial for your situation.
Understanding semen analysis results
A comprehensive semen analysis measures several key parameters. Here’s what doctors look for:
- Semen volume: 1.5 to 7.6 milliliters
- pH level: 7.2 to 8.0
- Sperm concentration: 15 to 259 million per milliliter
- Total sperm count: 39+ million per ejaculate
- Sperm motility (movement): 40% to 81%
- Progressive motility (forward swimming): 30%+
- Normal morphology (shape): 4%+
Bottom line: One abnormal result doesn’t necessarily indicate infertility. Sperm quality naturally fluctuates, which is why doctors often recommend two tests, 2-4 weeks apart, if the first shows concerning results.
Visual Signs: 8 signs of healthy sperm
What should you look for? Here are the key indicators of healthy sperm:
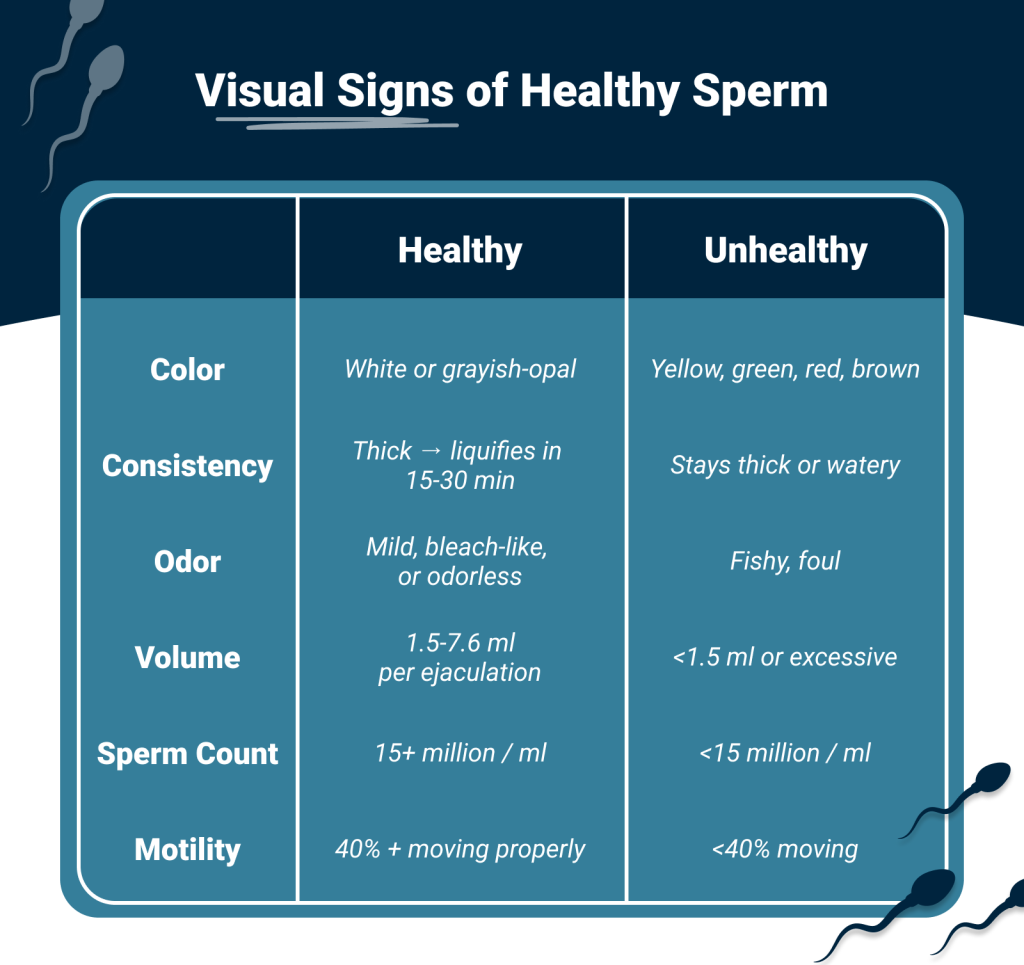
Bottom line: If your semen checks most of these boxes, you’re likely on the right track for reproductive health.
What Does Unhealthy Sperm Look Like?
Noticing something different about your semen can feel alarming—especially after months of trying without success. You might be wondering if what you’re seeing is the reason conception hasn’t happened yet. The truth is, many changes are temporary and treatable when caught early. Here’s what to watch for and what each sign might mean for your fertility.
Discoloration: Yellow, green, red, or brown semen
Semen that strays from the normal white-to-gray range often points to underlying problems. The color can give you clues about what’s happening:
Yellow semen: might result from jaundice, urine presence, prolonged abstinence, or high sulfur food consumption. If you’ve been timing sex around ovulation and waiting several days between attempts, that yellowish tint might simply be older semen—not necessarily a problem.
Pink, red, or brown semen usually means blood is present—potentially from prostate issues, infections, or trauma to the urethra. While seeing blood can be scary, many causes are treatable and don’t permanently affect fertility.
Dark brown or black semen may result from heavy bleeding or spinal cord injuries and requires immediate medical attention.
What to do: Document the color, when you first noticed it, and any other symptoms (pain, odor, fever). This information will be helpful to share with your doctor.
Watery or Chunky Texture: What it could mean
Texture changes can reveal important information about sperm health. Watery semen often indicates low sperm count—when there are fewer sperm present, the consistency becomes thinner than normal.
Remember, healthy semen should start thick, then liquefy within 30 minutes. Semen that stays thick well beyond this timeframe might suggest enzyme deficiencies or prostate problems. Chunky or clumpy textures often point to infections or blockages in the reproductive tract.
Foul Odor or Pain: Signs of infection or inflammation
While normal semen has that mild, slightly alkaline smell we discussed earlier, fishy or foul-smelling ejaculate typically suggests infections, possibly STIs. Pungent odors need prompt medical attention.
Pain during ejaculation combined with discolored semen strongly indicates inflammation or infection that requires professional assessment. Don’t ignore these symptoms—they’re your body’s way of signalling that something needs attention.
Low Volume or No Ejaculate: Retrograde ejaculation and other causes
Sometimes the issue isn’t what you see, but what you don’t see. Retrograde ejaculation occurs when semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis. This “dry orgasm” isn’t harmful to your health but may affect fertility since little or no sperm is ejaculated.
Other causes of unusually low volume include hormonal problems, blockages, or prostate inflammation. These issues can impact your ability to conceive and deserve medical evaluation.
Healthy sperm vs unhealthy sperm color comparison
The contrast between healthy and unhealthy semen is often striking. While healthy semen appears white to grayish, unhealthy sperm shows distinct visual differences that you can spot: yellow-green colors signal infections, red-brown tints indicate blood, watery consistency suggests low sperm count, and foul smells point to bacterial presence.
These warning signs matter because they can affect your fertility journey. If you notice any of these changes, especially when you’re trying to conceive, it’s worth discussing with your healthcare provider.

What affects sperm health the most?
Your sperm quality faces threats from multiple directions—some obvious, others surprising. Understanding these influences helps you take control of your fertility journey, but let’s be honest: some factors matter more than others.
Hormonal imbalances and low testosterone
Your reproductive system runs on precise hormone balance. When testosterone levels drop, sperm production follows—men with normal testosterone can produce over 15 million sperm per milliliter. This hormone is essential for creating sperm within your testes, directly affecting your fertility .
Conditions like hypogonadism can reduce both sperm production and sexual function. Other hormonal disruptions matter too: elevated prolactin or thyroid-stimulating hormone can negatively impact sperm parameters.
Lifestyle habits: smoking, alcohol, drugs
What you put into your body shows up in your sperm quality:
- Smoking decreases sperm count, motility, and normal shape —and the damage gets worse for moderate to heavy smokers. THC in cannabis is also problematic for sperm health
- Alcohol lowers testosterone production while increasing how quickly your body clears it
- Recreational drugs, including marijuana, reduce sperm motility, while cocaine decreases sperm viability
Medical conditions and medications
Chronic health issues create fertility complications. Diabetes can damage nerves controlling ejaculation. Chemotherapy drugs target rapidly dividing cells—including sperm—often causing temporary or permanent azoospermia.
Certain medications pose problems too. Antidepressants, blood pressure drugs, and testosterone replacement therapy can significantly reduce sperm quality.
Environmental and occupational exposures
Your environment affects your sperm more than you might think. Pesticides disrupt hormone function, while heavy metals induce oxidative stress. Heat exposure from laptops, saunas, and tight clothing impairs production—your testes function best at 2-4°C below body temperature.
Working with industrial chemicals or prolonged radiation exposure can permanently reduce sperm counts.
Track your fertility journey together with Premom’s tools as you make positive lifestyle changes.
Steps to support sperm count and motility

Good news: improving your sperm health doesn’t require drastic changes. Many of the most effective solutions are within your control, and small adjustments can yield significant results over time.
How to support sperm count naturally
Weight matters more than you might think. As BMI increases, sperm count typically decreases, so maintaining a healthy weight gives your swimmers a better chance.
What should you eat? Focus on a Mediterranean-style diet rich in fish (loaded with omega-3s), fresh fruits, vegetables, and walnuts. These antioxidant-rich foods help protect sperm from damage.
The habits that hurt most? Smoking(marijuana too!) tops the list—tobacco directly damages sperm DNA. Alcohol isn’t far behind, especially if you’re having 10+ drinks weekly, which lowers testosterone production.
Keep things cool down there. Your testes function best at 2-4°C below body temperature, so skip the hot tubs, saunas, and laptops on your lap.
How to increase sperm motility
Movement is energy, and energy comes from the right fuel. L-carnitine plays a crucial role in sperm metabolism, giving your sperm the energy they need to swim effectively.
Exercise helps, but don’t overdo it. Light to moderate activity supports motility, while intense workouts can actually work against you. Sleep matters too—aim for 7-8 hours nightly as it directly impacts how well your sperm move.
What Vitamins and Supplements Help Improve Sperm Health
The research on fertility supplements is promising, and many men see measurable improvements within 2-3 months of consistent use. Here’s what studies show can help:
- Vitamin C: 2,000mg daily improved motility by over 90%
- CoQ10 (As ubiquinol, ideally): Increased motility by over 50%
- Zinc& Selenium: Particularly beneficial if you’re deficient
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Ranked highest for improving concentration
- Ashwagandha: Showed a 57% increase in motility after three months
Getting started with supplements: Premom’s Sperm Fortify is a daily oral supplement for men that supports sperm health and reproductive potential. It contains doctor formulatedingredients such as acetyl L-carnitine, CoQ10 (as ubiquinol) , zinc, selenium, antioxidants A,C&E and KSM-66 (R) ashwaganda to help support sperm count, motility, and morphology during preconception efforts!*
Since it takes 64-74 days to produce new sperm, give any supplement routine at least 2-3 months before evaluating effectiveness and always talk to your healthcare provider before starting a supplement regimen. Track your supplement intake and any changes you notice in Premom’s health log—this creates a clear timeline when you get follow-up semen analysis results.
When to see a fertility specialist
The standard recommendation is to seek help after 12+ months of trying (or 6+ months if your partner is 35 or older). But if you’re reading this article, you’re probably wondering whether you should wait that long—especially if you’ve already been trying for several months and suspect male fertility might be the issue.
Don’t wait the full 12 months if:
- You already know about low sperm count from previous testing
- You have a history of testicular trauma, surgery, or cancer treatment
- You’re experiencing erectile dysfunction or ejaculation problems
- Your partner has been tracking ovulation consistently and timing is likely confirmed with BBT or PdG tests, yet conception hasn’t occurred after 6+ cycles
- You’ve noticed significant changes in semen appearance, volume, or consistency
- You have chronic health conditions known to affect fertility (diabetes, hormonal issues)
Fertility specialists can assess the severity of potential male factor issues through comprehensive semen analysis and hormone testing. Based on results, they’ll suggest solutions ranging from lifestyle modifications and supplements to medical treatments or advanced assisted reproduction techniques like IUI or ICSI.
Before your appointment, be sure to bring your Premom tracking data showing lifestyle factors, any at-home observations, and your partner’s ovulation tracking history. This comprehensive picture helps your provider understand the full context and recommend the most appropriate next steps.
What’s Your Next Step to Improve Sperm Health?
Sperm health is a window into your overall wellness and your future child’s development. The difference between healthy and unhealthy sperm isn’t just about conceiving faster—it’s about taking control of your reproductive potential.
Simple lifestyle changes make a real difference: maintaining a healthy weight, eating nutrient-rich foods, limiting alcohol, and avoiding excess heat. Supplements like vitamin A,C & E,, CoQ10, and zinc show promise for naturally supportingsperm parameters.
Remember that sperm production takes about 2+ months, so be patient with your improvements. Track your fertility journey together using Premom’s PreDad feature to monitor progress while making lifestyle changes alongside your partner.
If concerns persist after lifestyle modifications—especially after trying for 12+ months—consult a fertility specialist. Many male fertility issues respond well to early treatment.
Ready to optimize your fertility? Download Premom free today and take the male fertility self-assessment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sperm Health
Healthy sperm typically appear whitish-gray or slightly cloudy with a jelly-like texture. It should have a mild, slightly alkaline odor often compared to ammonia or chlorine. However, a comprehensive semen analysis is the most accurate way to assess sperm health, measuring factors like count, motility, and morphology.
Signs of unhealthy sperm may include unusual color (yellow, green, red, or brown), consistently thick or watery consistency, or a foul or fishy odor. Low sperm count, poor motility, and abnormal morphology are also indicators, but these require professional testing to detect.
Lifestyle factors significantly impact sperm health. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and recreational drug use can decrease sperm count and motility. Maintaining a healthy weight, following a nutrient-rich diet, and avoiding excessive heat exposure to the testicles can improve sperm quality.
Yes, you can improve sperm health naturally through lifestyle changes. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a Mediterranean diet rich in antioxidants, quitting smoking, moderating alcohol intake, and getting regular exercise. Certain supplements like vitamin C, CoQ10, and zinc may also help enhance sperm parameters.
You should consider consulting a fertility specialist if you’ve been trying to conceive for 12 months or more without success (6 months if your partner is 35 or older). Other reasons to seek professional help include a known low sperm count, a history of testicular trauma, erectile dysfunction, or ejaculation problems.
References
Akhatova A, Jones C, Coward K, et al. How do lifestyle and environmental factors influence the sperm epigenome? Effects on sperm fertilising ability, embryo development, and offspring health. Clin Epigenetics. 2025;17(1):7.
Jensen TK, Jacobsen R, Christensen K, Nielsen NC, Bostofte E. Good Semen Quality and Life Expectancy: A Cohort Study of 43,277 Men. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170(5):559-565.
Omu AE. Sperm Parameters: Paradigmatic Index of Good Health and Longevity. Med Princ Pract. 2013;22(Suppl 1):30-42.
Mason MM, Schuppe K, Weber A, et al. Ejaculation: The process and characteristics from start to finish. Curr Sex Health Rep. 2023;15:1-9.
Akmal M, Qadri JQ, Al-Waili NS, et al. Improvement in human semen quality after oral supplementation of vitamin C. J Med Food. 2006;9(3):440-2.
World Health Organization. WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen. 6th ed. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2021.
Chen PC, Chen YJ, Yang CC, et al. Male Infertility Increases the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Taiwan. World J Mens Health. 2022;40(3):490-500.
Lafuente R, González-Comadrán M, Solà I, et al. Coenzyme Q10 and male infertility: a meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30(9):1147-56.
Fallah A, Mohammad-Hasani A, Hosseinzadeh Colagar A. Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men’s Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization. J Reprod Infertil. 2018;19(2):69-81.
Safarinejad MR. Effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on semen profile and enzymatic anti-oxidant capacity of seminal plasma in infertile men with idiopathic oligoasthenoteratospermia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised study. Andrologia. 2011;43(1):38-47.
Wankhede S, Langade D, Joshi K, et al. Clinical Evaluation of the Spermatogenic Activity of the Root Extract of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) in Oligospermic Males: A Pilot Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:571420.
Wessel L. Infertile men have a higher risk of heart disease, diabetes, study finds. Stanford Medicine News Center. December 7, 2015. Accessed December 8, 2025. https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2015/12/infertile-men-have-a-higher-risk-of-heart-disease-diabetes.html.
Huang R, Chen J, Guo B, et al. Diabetes-induced male infertility: Potential mechanisms and treatment options. Mol Med. 2024;30(1):11.
Balawender K, Orkisz S. The impact of selected modifiable lifestyle factors on male fertility in the modern world. Cent Eur J Urol. 2020;73(4):563-568.



